Hybrid Networking in AWS
AWS Direct Connect
- Direct Connect allows for private communication over a dedicated line, and can provide additional security, performance, and privacy.
- It can also bridge the network architecture gap between on-premises networks and AWS.
- Direct Connect locations are public datacenters that have AWS operated private backbone connectivity to AWS regions.
- A virtual interface (VIF) is a virtual interface (802.1Q VLAN and a BGP session.)
- Virtual interfaces can be private or public.
- A Private virtual interfaces (Private VIF) connects to a single VPC in the same AWS Region using a VGW.
- A Public virtual interfaces (public VIF) can be used to connect to AWS Public Services in any Region (but not the internet).
- Key requirement: Your device must support Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and BGP MD5 authentication.
- DX Connections are NOT encrypted. Use an IPSec site-to-site VPN over a VIF to add encryption in transit.
- LAG - Used to combine multiple physical connections into a single logical connection using LACP - provides improved speed
- Can use Site-to-site VPN as a backup path for primary DX Connection (High Availability at a lower cost than DX-DX architecture) - DO NOT use this architecture if you need speed above 1Gbps
To connect to services such as EC2 using just Direct Connect you need to create a private virtual interface. However, if you want to encrypt the traffic flowing through Direct Connect, you will need to use the public virtual interface of DX to create a VPN connection that will allow access to AWS services such as S3, EC2, and other services. Direct Connect in itself does not provide encryption in-transit.

If you want a short-term or lower-cost solution, you might consider configuring a hardware VPN as a failover option for a Direct Connect connection. VPN connections are not designed to provide the same level of bandwidth available to most Direct Connect connections. Ensure that your use case or application can tolerate a lower bandwidth if you are configuring a VPN as a backup to a Direct Connect connection.
For consistent, reliable, and redundant connectivity, install a second DX connection from a different network carrier. You can attach it to the same virtual private gateway as the first DX connection.
Direct Connect Gateways
- A Direct Connect gateway is a globally available resource. You can create the Direct Connect gateway in any Region and access it from all other Regions.
- A Direct connect Gateway is associated with either of the following:
- A transit gateway when you have multiple VPCs in the same Region
- A virtual private gateway
- Network traffic can be routed from on-premises to any VPC across regions. However, DX Gateway does not allow inter-vpc communication among VGWs.
AWS Managed VPN can be combined with Direct Connect Gateway to provide an IPSEC-encrypted private connection
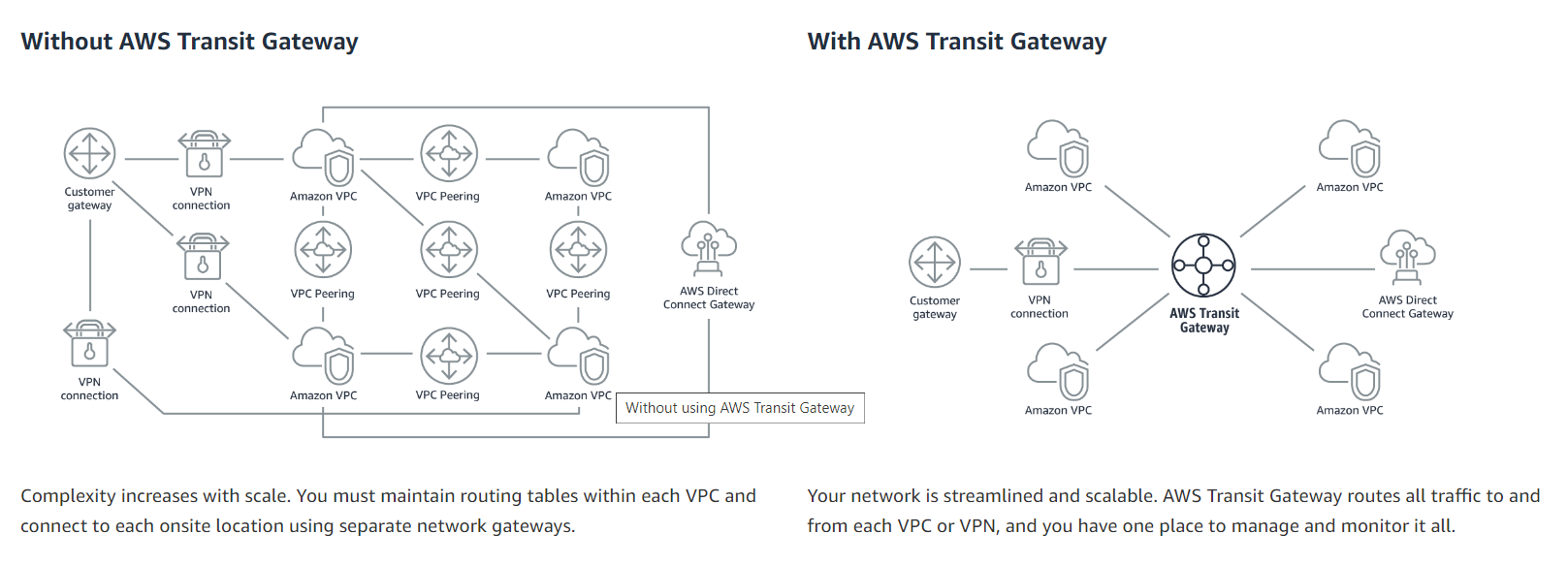
Transit Gateway
- AWS Transit Gateway connects your Amazon Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and on-premises networks through a central hub. Your data is automatically encrypted and never travels over the public internet.
- A route table includes dynamic and static routes that decide the next hop based on the destination IP address of the packet.
- Attachments: A Transit Gateway can be attached to one of the following:
- One or more VPC - AWS Transit Gateway deploys an elastic network interface within VPC subnets, which is then used by the transit gateway to route traffic to and from the chosen subnets.
- A Connect SD-WAN/third-party network appliance
- An AWS Direct Connect gateway. In this configuration, Corporate office is connected to a DX Gateway which is connected to TGW. Transit VIF is used.
- A peering connection with another transit gateway
- A VPN connection to a transit gateway
- Transit Gateway with Direct Connect Gateway supports full transitive routing between on-premises, TGW and VPCs.
- Example configurations
- Centralized Router
- Isolated VPCs
- Isolated VPCs with shared services
- Peering
- Centralized outbound routing
- Appliance VPC
Use Cases
- Centralized Router: In this scenario, TGW acts as a simple layer 3 IP router connecting all VPCs, AWS Direct Connect and Site-to-Site VPN Connections.
- Isolated VPCs: In this scenario, TGW acts as multiple isolated routers for isolated VPCs. Outbound traffic is routed through TGW, but VPCs cannot communicate with each other.
- Isolated VPCs with shared services: In this scenario, isolated VPCs can connect to a shared services VPC through TGW, but cannot communicate with each other. (they are blocked because there is no route for them in the transit gateway route table)
- Peering: In this scenario, two TGWs are connected with each other, providing transitive peering across resources connected to each of the TGW.
- Centralized outbound routing to the internet: In this scenario, outbound traffic from private subnets are routed to TGW, which in turns routes the request to a VPC that contains NAT Gateway and Internet Gateway.
- Appliance VPC: In this use case, multiple VPC outbound traffic is routed to transit gateway (TGW), which in turn routes traffic to a VPC which contains a security appliance that inspects traffic. The appliance is a stateful appliance, therefore both the request and response are inspected.
Sharing
- Use Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Site-to-Site VPN connections.
- Associate the same VPC route table with all of the subnets that are associated with the transit gateway, unless your network design requires multiple VPC route tables.
- You can use AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM) to share a transit gateway for VPC attachments across accounts or across your organization in AWS Organizations.
Flow Logs
- Transit Gateway Flow Logs is a feature that enables you to capture information about the IP traffic going to and from your transit gateways. Flow log data can be published to Amazon CloudWatch Logs or Amazon S3.
Monitoring
- Transit Gateway can be monitored through Cloudwatch Logs and CloudTrail Logs. All calls to transit gateway actions are logged by CloudTrail.
Design Best practices
- Use a separate (small) subnet for each TGW subnet attachment
- Create one network ACL and associate it with all of the subnets that are associated with the transit gateway.
- Use Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Site-to-Site VPN connections.
- Associate the same VPC route table with all of the subnets that are associated with the transit gateway, unless your network design requires multiple VPC route tables.
S3endpoints
- With S3 endpoints, you can create a private route in your VPC that allows you to route traffic directly to and from S3 in your VPC.
- S3 was the first AWS service with endpoints, and AWS is constantly evaluating endpoints for other services.
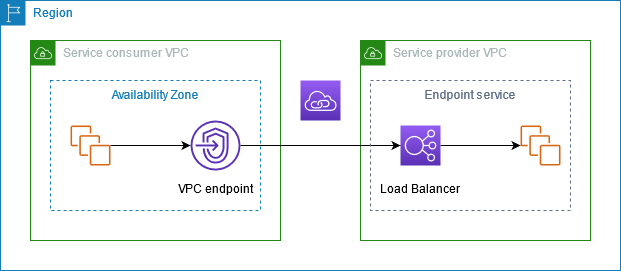
AWS PrivateLink
- Service consumers create interface VPC endpoints to connect to endpoint services that are hosted by service providers.
- Interface endpoint vs Gateway endpoint. Gateway endpoint is for just S3 and DynamoDB using Private IP Addresses and uses Route Table. On the other hand, Interface endpoint uses NLB for routing.
Global Accelerator
- Two single IP that can in turn be connected to Load Balancers and put origin servers behind this
- Leverage jitter and congestion free aws network to origin servers
- Use cases:
- Scale for increased application utilization
- Acceleration for latency-sensitive applications
- Disaster recovery and multi-Region resiliency (if compute resources in one region fails, it can be rerouted to another region)
- Global Accelerator decreases the risk of attack by masking your origin behind two static entry points. These entry points are protected by default from Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks with AWS Shield.
- Using a custom routing accelerator, you can leverage the performance benefits of Global Accelerator for your VoIP or gaming applications.
Site to Site VPN
A virtual private gateway is the VPN concentrator on the Amazon side of the Site-to-Site VPN connection. You create a virtual private gateway and attach it to the VPC from which you want to create the Site-to-Site VPN connection.
- Static Routing
- Dynamic Routing: BGP (Border Gateway Protocol). Routing tables are updated automatically. Just need to specify the ASN (Autonomous System Number) of the CGW and VGW.
Only one virtual private gateway (VGW) can be attached to a VPC at a time. Site to Site VPN and Internet access to corporate data center can be facilitated by NAT instance, but not through NAT Gateway.
Network to Amazon VPC Connectivity Options
AWS Direct Connect + VPN
This solution combines the benefits of the end-to-end secure IPSec connection with low latency and increased bandwidth of the AWS Direct Connect to provide a more consistent network experience than internet-based VPN connections.
AWS Direct Connect public VIF establishes a dedicated network connection between your network to public AWS resources, such as an Amazon virtual private gateway IPsec endpoint.
AWS Direct Connect + Transit Gateway
This solution simplifies management of connections between an Amazon VPC and your networks over a private connection that can reduce network costs, increase bandwidth throughput, and provide a more consistent network experience than internet-based connections.
AWS Direct Connect + TGW + VPN
Consider taking this approach when you want to simplify management and minimize the cost of IPSec VPN connections to multiple Amazon VPCs in the same region, with the low latency and consistent network experience benefits of a private dedicated connection over an internet-based VPN.
AWS VPN CloudHub
Use this approach if you have multiple branch offices and existing internet connections and would like to implement a convenient, potentially low-cost hub-and-spoke model for primary or backup connectivity between these remote offices.
AWS TGW + VPN
Consider using this approach when you want to take advantage of an AWS-managed VPN endpoint for connecting to multiple VPCs in the same region without the additional cost and management of multiple IPSec VPN connections to multiple Amazon VPCs.
VPC to VPC Connectivity options
AWS PrivateLink
We recommend this approach if you want to use services offered by another VPC securely within the AWS network, with all network traffic staying on the global AWS backbone and never traversing the public internet.
Transit Gateway
AWS Transit Gateway is a highly available and scalable service to consolidate the AWS VPC routing configuration for a region with a hub-and-spoke architecture.
Each VPC need not have a NAT Gateway. The egress traffic can be routed into Transit Gateway & onto other VPCs.
Software Site-to-Site VPN
This option is recommended when you want to manage both ends of the VPN connection using your preferred VPN software provider. This option uses an internet gateway attached to each VPC to facilitate communication between the software VPN appliances.